Table of Contents
- Materials in Hexagon
Hexagon is a 3D modeler and does not have a built-in renderer. You can, however, prepare your models with textures in order to advance the texturing at the same time as you finalize the form of the model. Defining materials on an object is also needed to paint colors and textures.
A material is the visual characteristics of an object, regrouping:
In these last two types, you can control the repetition of a pattern or image, and the way it merges with the base color of the object.
Remark:
When you create an object, it has applied to it a default material of a flat light grey color. This material cannot be modified, and does not appear in the material list. To customize the object material, it is necessary to create a new material attached to this object.
You can edit materials in the materials palette, in the materials panel on the left of the screen (by default) or through the “Windows” pull-down menu, then choosing “Materials”.
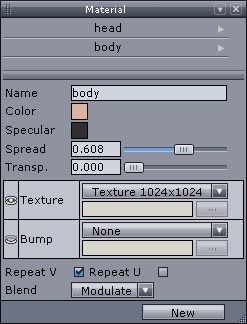
The material panel.
Note: If no material has been created, the window is empty.
There must be a selected object in the scene in order to create a new material.
Once the material has been created, several operations can be performed, accessible through a pull-down menu, by clicking on the small arrow located to the right of the material name:
Hexagon lets you place several materials on different parts of the same object. To do this, you will create shading domains. These are zones (polygon faces) on which you can place a material different than the base material of the object.
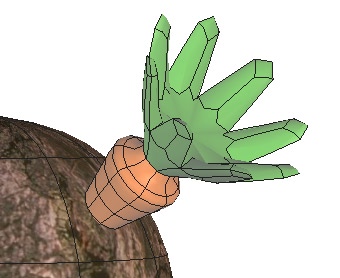
An object with two domains.
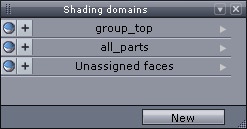
The shading domains palette.
Remark:
Once a domain has been created, several operations can be performed. They can be accessed through a pull-down menu, by clicking on the small arrow located to the right of the domain name: